Shrimp keeping, like any specialized hobby, comes with its own unique set of terms and jargon. These terms can often confuse beginners and even those who have been in the hobby for a while. For instance, have you ever wondered what ‘molting’ or ‘berried’ means in the context of shrimp keeping? Well, you’re not alone.
In this post, we’ll demystify standard shrimp-keeping terms, providing you with a handy glossary to refer to as you navigate the fascinating world of shrimp-keeping.
My Journey into the World of Shrimp Keeping
I remember when I first dipped my toes into the world of shrimp keeping. It was about 20 years ago, and I was immediately captivated by these tiny aquatic creatures’ vibrant colors and fascinating behaviors. However, as I delved deeper into the hobby, I quickly realized that there was a whole new language I needed to learn.
In the early days, I constantly looked up terms online, trying to decipher what other shrimp keepers were talking about in forums and articles. Terms like ‘cycling’, ‘TDS’, and ‘substrate’ were all Greek to me. But, with time and a lot of patience, I gradually began to understand and speak this unique language.
After years of experience and countless hours spent researching and observing my own shrimp, I feel confident I understand these terms. But I know the struggle of being a beginner, of feeling lost in a sea of unfamiliar jargon. That’s why I’ve decided to compile this glossary of shrimp-keeping terms. I hope it will serve as a helpful reference for beginners and seasoned shrimp keepers alike.
So, without further ado, let’s dive into the world of shrimp-keeping terminology!
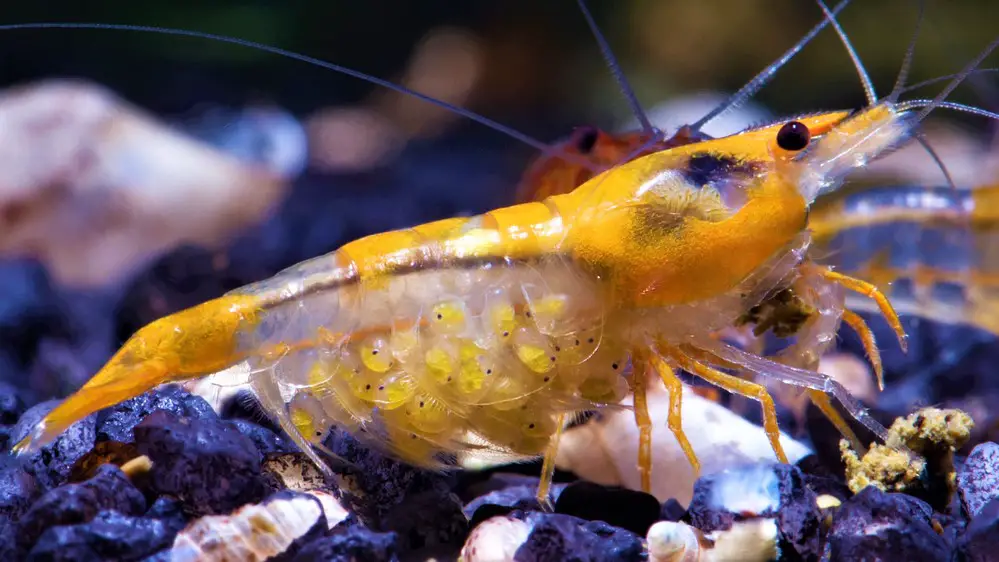

Glossary
- Acclimation: The process of gradually introducing a shrimp to new water conditions.
- Additives: Substances added to the aquarium water to improve the health of the shrimp.
- Adult: a fully mature shrimp that is ready to breed and lay eggs
- Air stone: a small, porous object that is connected to an air pump
 and releases bubbles into the water, helping to oxygenate the aquarium and circulate water
and releases bubbles into the water, helping to oxygenate the aquarium and circulate water - Algae: A simple non-flowering plant of a large group that includes the seaweeds and many single-celled forms. Algae contain chlorophyll but lack true stems, roots, leaves, and vascular tissue.
- Amano Shrimp: A popular freshwater shrimp named after Takashi Amano who made them popular in the hobby.
- Antennae: Long, thin sensory appendages on the head of a shrimp that they use to sense their environment.
- Aquascape: The craft of arranging aquatic plants, as well as rocks, stones, cavework, or driftwood, in an aesthetically pleasing manner within an aquarium.
- Bacterium/bacteria: microscopic organisms that play a critical role in maintaining the health and balance of an aquarium ecosystem, breaking down waste and harmful compounds and converting them into less harmful forms
- Berried: A term used to describe a female shrimp carrying eggs.
- Biofiltration: the process of using beneficial bacteria to break down harmful compounds like ammonia and nitrite in an aquarium, converting them into less harmful compounds like nitrate
- Biofilm: A thin layer of microorganisms that forms on surfaces in contact with water.
- Carapace: The hard, protective outer shell that covers the front part of a shrimp, including the head and thorax.
- Caridina: A genus of shrimp in the family Atyidae of the order Decapoda.
- Cephalothorax: The fused head and thorax of a shrimp.
- Cheliped: The first pair of legs on a shrimp, which end in claws and are used for feeding and defense.
- Cherry Shrimp: A variety of freshwater shrimp from Taiwan which is commonly kept in aquariums. The natural coloration of the shrimp is green-brown. There are various colors such as red, yellow, orange, green, blue, violet, black, etc.
- CO2: carbon dioxide, a gas that is sometimes added to aquariums to promote plant growth and maintain pH stability
- Conductivity: conductivity is a measure of the water’s ability to conduct an electrical current, which is influenced by the amount of dissolved salts and other ionizable substances in the water.
- Cull: a term used to describe removing or selling lower-quality shrimp from a breeding population in order to improve overall genetics and quality of offspring
- Cycling: The process of establishing bacterial colonies in an aquarium before adding shrimp or fish.
- Dead spot: an area in an aquarium where water circulation is poor or non-existent, which can lead to the accumulation of detritus and the growth of harmful bacteria and other organisms
- Dechlorinator: a chemical solution used in aquariums to remove chlorine and chloramine from tap water, which can be toxic to shrimp and other aquatic life.
- Detritus: Organic waste material from decomposing plants or animal matter. This includes feces and dead organisms.
- Dwarf Shrimp: Small shrimp that grow up to 2 inches in size.
- Exoskeleton: The hard, protective outer shell that covers a shrimp’s body.
- F1 generation: the first generation of offspring produced by a particular pair of shrimp, which are typically considered to be of higher quality and more genetically diverse than subsequent generations
- Filial (F1, F2, F3, etc): F1 stands for Filial 1 (or first filial). Filial is a word used to describe sons and daughters, and it means the first generation from a genetic cross between parents.
- GH: General hardness, which refers to the concentration of minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium, in water
- Gills: The organs that shrimp use to extract oxygen from water.
- Ghost Shrimp: A type of freshwater shrimp that is known for its transparent body.
- HOB filter: Hang-on-back filter, which is a type of aquarium filter that hangs on the back of the tank and uses a pump to circulate and filter water
- Hardness: The measure of the amount of calcium and magnesium in water.
- Invertebrate: an animal without a backbone, such as shrimp, snails, and other aquatic life commonly kept in aquariums
- KH: Carbonate hardness, which refers to the concentration of carbonate and bicarbonate ions in water, which can affect pH stability and buffering capacity
- Lighting: the type and intensity of light used in an aquarium, which can affect plant growth, algae growth, and the behavior and activity of shrimp and other aquatic life
- Mischling: Mischling is a German word for “crossbreed”. A mischling (in the shrimp hobby) is a hybrid cross between Crystals and Taiwan Bees.
- Molting: The process where shrimp shed their exoskeleton to grow.
- Neocaridina: A genus of shrimp that are commonly kept in the aquarium hobby. Examples include the Cherry Shrimp and Blue Dream Shrimp.
- Nitrite: a toxic compound that can form in an aquarium as a result of the breakdown of harmful compounds like ammonia, and can cause harm or death to shrimp and other aquatic life
- Ovaries: the reproductive organs of female shrimp, where eggs are produced and stored until they are ready to be fertilized
- pH: the measure of the acidity or alkalinity of water, which can affect the health and behavior of shrimp and other aquatic life
- Pinto: A Pinto is a colour variation and type of Taitibee. There are 3 variants of patterns: Spotted Head, Zebra, and Fancy (such as skunk pattern and cloud patterns).
- Pleopods (Swimmerets): Small, leg-like appendages on the underside of a shrimp’s body that are used for swimming and, in females, for carrying eggs.
- Selective breeding: the process of intentionally breeding shrimp with desirable traits, such as color, pattern, size, or behavior, in order to improve the overall quality and genetic diversity of a population.
- Sponge filter: a type of aquarium filter that uses a sponge to filter and purify water, and can provide a habitat for beneficial bacteria that help break down harmful compounds in the water
- Subadult: a term used to describe a shrimp that has molted and grown to a size larger than a juvenile, but is not yet fully mature or ready to breed
- Substrate: the material that is placed on the bottom of an aquarium, which can affect water quality, plant growth, and the behavior and activity of shrimp and other aquatic life
- TDS: total dissolved solids, which refers to the concentration of dissolved minerals and other substances in water, and can be used as an indicator of water quality in aquariums.
- Tibee: A hybrid between any Tiger shrimp and usually a Taiwan Bee (TB) or Crystals (CBS – Crystal Black Shrimp and CRS – Crystal Red Shrimp).
- TaiTibee: A Taitibee is a Tibee crossed back with a Taiwan Bee.
- Uropods: The large, flat appendages on the last segment of a shrimp’s body, which form part of the tail fan
 and are used for rapid backwards movement.
and are used for rapid backwards movement.

Conclusion & Call to Action
Understanding the specific terminology used in shrimp keeping is crucial for both beginners and experienced hobbyists. It helps you communicate effectively with other shrimp keepers and enhances your understanding and enjoyment of this fascinating hobby.
Remember, every expert was once a beginner who didn’t know what ‘molting’ or ‘berried’ meant. So, don’t be discouraged if you’re still learning the ropes. With time, patience, and a little help from resources like this glossary, you’ll soon be speaking the language of shrimp keeping like a pro.
Don’t hesitate to reach out if you need help understanding a term or concept. I’m always here to help fellow shrimp enthusiasts navigate this exciting hobby. And if you can’t reach me here, be sure to check out the Aquarium Shrimp Keeping group on Facebook. It’s a wonderful community of shrimp keepers who are always willing to share their knowledge and experience.
Finally, remember that the journey is just as important as the destination. So, take your time, enjoy the process, and most importantly, have fun. After all, that’s what hobbies are for, right?
Happy Shrimp Keeping!
